Stress fractures on the top of your foot can be confusing, often resembling bruises. Discover the signs, causes, and treatment options in our comprehensive guide.
What is a Stress Fracture?
Stress fractures are tiny cracks in a bone caused by repetitive force, often from overuse, such as repeatedly jumping up and down or running long distances. Unlike acute fractures, which are caused by a single, severe impact, stress fractures result from cumulative stress that exceeds the bone’s ability to repair itself. These injuries commonly occur in weight-bearing bones, such as those in the foot, due to the constant pressure and impact they endure.
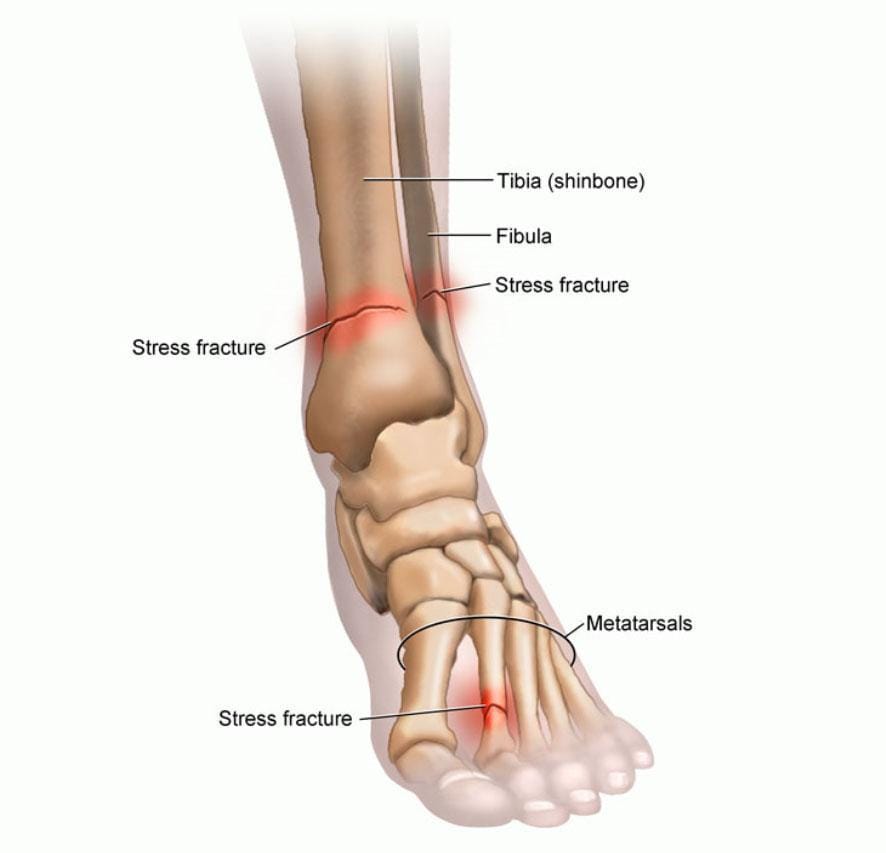
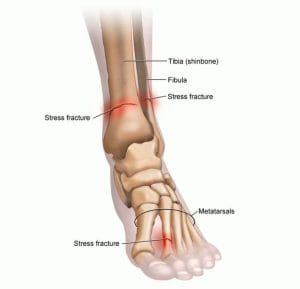
The human foot comprises 26 bones, making it a complex and integral part of the body. When subjected to continuous strenuous activities, certain bones in the foot, especially the metatarsals, are more susceptible to stress fractures. The metatarsals are a group of five long bones in the midfoot that connect the ankle to the toes. These bones play a critical role in balancing and movement, making them prone to stress-related injuries.
Stress fractures can be a source of significant discomfort and, if left untreated, can lead to more severe complications. Understanding the nature of stress fractures is essential for recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment. This knowledge can also help individuals take preventive measures to avoid such injuries in the future.
Common Causes of Stress Fractures in the Foot
Stress fractures are often the result of repetitive activities that place excessive strain on the foot. One of the most common causes is engaging in high-impact sports such as running, basketball, and soccer. These activities involve frequent jumping and sudden changes in direction, which can put immense pressure on the bones in the foot. Athletes who increase their training intensity or duration too quickly without allowing their bodies to adapt are particularly at risk.
Improper footwear is another significant factor contributing to stress fractures. Shoes that do not provide adequate support, cushioning, or fit can lead to increased stress on the foot bones. For instance, wearing worn-out running shoes that no longer absorb shock effectively can cause undue pressure on the metatarsals. Additionally, high heels or shoes with insufficient arch support can alter the natural biomechanics of the foot, leading to stress injuries over time.
Certain medical conditions and lifestyle factors can also predispose individuals to stress fractures. Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones, can make bones more susceptible to fractures from minor stresses. Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in calcium and vitamin D, can impair bone health and increase the risk of fractures. Furthermore, sudden changes in physical activity levels, such as transitioning from a sedentary lifestyle to an active one without proper conditioning, can also contribute to the development of stress fractures.
Symptoms of Stress Fracture Bruises
Stress fracture bruises on the top of the foot can present a variety of symptoms that often mimic those of other foot injuries, making diagnosis challenging. One of the most common symptoms is localized pain that worsens with weight-bearing activities and improves with rest. This pain is usually described as a dull ache that gradually intensifies over time. Unlike acute fractures, stress fractures may not cause immediate, sharp pain but instead develop gradually as the bone undergoes repetitive stress.
Swelling and tenderness are also common symptoms of stress fractures. The affected area may become swollen and tender to the touch, and the skin may appear red or inflamed. In some cases, a visible bruise may form on the top of the foot, which can be mistaken for a simple contusion. However, unlike typical bruises, the pain associated with a stress fracture does not subside with time and may worsen with continued activity.
Another symptom to be aware of is the presence of a “hot spot” on the foot. This refers to a specific area that feels warm to the touch and is particularly painful when pressure is applied. This localized warmth and pain are indicative of the body’s inflammatory response to the micro-damage occurring in the bone. Recognizing these symptoms and seeking medical attention promptly is crucial to prevent further damage and ensure proper healing.
How to Differentiate Between a Bruise and a Stress Fracture
Distinguishing between a bruise and a stress fracture can be challenging, as both conditions can present with similar symptoms such as pain, swelling, and discoloration. However, there are key differences that can help in identifying a stress fracture. One of the primary differences is the nature and duration of the pain. While a bruise typically results from a direct impact and causes immediate pain that gradually subsides, a stress fracture causes pain that develops gradually and intensifies with continued activity.

Another distinguishing factor is the location and pattern of swelling. Bruises often cause diffuse swelling and discoloration over a broader area, whereas stress fractures typically cause more localized swelling and tenderness. The presence of a “hot spot” or a specific area of warmth and increased pain is also more indicative of a stress fracture than a simple bruise. Additionally, stress fractures often cause pain during weight-bearing activities and may result in an altered gait or limping.
Diagnostic imaging can also play a crucial role in differentiating between the two conditions. While X-rays may not always detect stress fractures in their early stages, advanced imaging techniques such as MRI or bone scans can provide a more accurate diagnosis. These imaging methods can reveal the presence of micro-cracks in the bone and any associated swelling or inflammation. Consulting with a healthcare professional and undergoing appropriate diagnostic tests is essential for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
Diagnosis: How Healthcare Professionals Identify Stress Fractures
Diagnosing a stress fracture involves a combination of a thorough medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies. During the medical history, the healthcare professional will inquire about the patient’s symptoms, recent activities, and any previous injuries. Understanding the patient’s activity level, training regimen, and any changes in physical activity can provide valuable insights into the potential causes of the stress fracture.
A physical examination is conducted to assess the affected area for tenderness, swelling, and any visible signs of injury. The healthcare professional may apply pressure to specific areas of the foot to identify points of tenderness and localized pain. They may also evaluate the patient’s gait and weight-bearing abilities to determine the impact of the injury on mobility. The presence of a “hot spot” or a specific area of warmth and increased pain can also aid in the diagnosis.
Imaging studies are crucial for confirming the presence of a stress fracture and determining its severity. X-rays are typically the first imaging modality used, but they may not always detect stress fractures in their early stages. If the X-ray results are inconclusive, advanced imaging techniques such as MRI or bone scans may be recommended. MRI is particularly effective in identifying stress fractures, as it can reveal both bone and soft tissue abnormalities. Bone scans can also detect areas of increased bone activity, indicating the presence of a stress fracture.
Treatment Options for Stress Fracture Bruises
Treating stress fracture bruises involves a combination of rest, immobilization, and pain management. Rest is the cornerstone of treatment, as it allows the bone to heal and prevents further damage. Patients are advised to avoid weight-bearing activities and any activities that exacerbate the pain. Depending on the severity of the stress fracture, crutches or a walking boot may be recommended to immobilize the foot and reduce stress on the affected area.
Pain management is another critical aspect of treatment. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. However, it is essential to avoid excessive use of NSAIDs, as they can potentially interfere with bone healing. Applying ice to the affected area can also help reduce swelling and provide temporary pain relief. Ice should be applied for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
In some cases, physical therapy may be recommended to aid in the recovery process. Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the injured area, improve flexibility, and restore normal movement patterns. A physical therapist can also provide guidance on gradually resuming activities and implementing proper techniques to prevent future injuries. It is essential to follow the healthcare professional’s recommendations and allow adequate time for the bone to heal before returning to regular activities.
Recovery Time and Rehabilitation
The recovery time for stress fracture bruises can vary depending on the severity of the injury and the individual’s overall health. On average, it takes about 6-8 weeks for a stress fracture to heal, but this timeline can be longer for more severe fractures or if proper rest and treatment are not adhered to. During this period, it is crucial to follow the healthcare professional’s recommendations and avoid activities that put stress on the affected foot.
Rehabilitation plays a vital role in the recovery process and involves a gradual return to normal activities. Physical therapy is often an integral part of rehabilitation, focusing on strengthening the muscles surrounding the injured area, improving flexibility, and restoring normal movement patterns. A physical therapist can design a personalized rehabilitation program that includes exercises to enhance balance, coordination, and overall foot strength.
Gradual progression is essential during rehabilitation to prevent re-injury. Patients are advised to start with low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling before gradually transitioning to weight-bearing activities. It is crucial to listen to the body and avoid pushing through pain, as this can delay the healing process and increase the risk of complications. Regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare professional are necessary to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to the rehabilitation program.
Preventing Stress Fractures in the Future
Preventing stress fractures involves a combination of proper training techniques, appropriate footwear, and maintaining overall bone health. One of the most effective ways to prevent stress fractures is to gradually increase the intensity and duration of physical activities. This allows the body to adapt to the increased stress and reduces the risk of overuse injuries. Incorporating rest days into the training schedule is also crucial to allow the body to recover and repair.
Wearing appropriate footwear is essential for preventing stress fractures. Shoes should provide adequate support, cushioning, and fit to reduce the impact on the foot bones. It is important to replace worn-out shoes regularly, as they lose their shock-absorbing properties over time. For individuals with specific foot mechanics, custom orthotics may be recommended to provide additional support and correct any biomechanical imbalances.
Maintaining overall bone health is vital for preventing stress fractures. A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is essential for bone strength and density. Weight-bearing exercises such as walking, running, and strength training can also help improve bone health. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption is crucial, as these habits can negatively impact bone health. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can help identify any underlying conditions that may predispose individuals to stress fractures and allow for early intervention.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience persistent pain on the top of your foot that does not improve with rest or if you notice swelling, tenderness, or a “hot spot” in the affected area. Early intervention is crucial to prevent further damage and ensure proper healing. Ignoring the symptoms or delaying treatment can lead to more severe complications, such as a complete fracture or chronic pain.
If you have a history of stress fractures or other bone-related conditions, it is particularly important to seek medical attention at the first sign of symptoms. Individuals with conditions such as osteoporosis or nutritional deficiencies are at a higher risk of developing stress fractures and may require specialized treatment and monitoring. Additionally, athletes or individuals who engage in high-impact activities should be proactive in seeking medical attention to address any potential overuse injuries promptly.
During the medical appointment, the healthcare professional will conduct a thorough evaluation, including a physical examination and possibly imaging studies, to determine the cause of the symptoms and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Following the healthcare professional’s recommendations and adhering to the prescribed treatment plan is essential for a successful recovery and preventing future injuries.
Managing Foot Health and Injury Prevention
Understanding stress fracture bruises on the top of your foot is crucial for recognizing symptoms early, seeking appropriate treatment, and preventing future injuries. Stress fractures result from repetitive stress on the bones, often caused by high-impact activities, improper footwear, and underlying medical conditions. Recognizing the symptoms, such as localized pain, swelling, and tenderness, and differentiating them from simple bruises can help in seeking timely medical attention.
Proper diagnosis through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies is essential for confirming the presence of a stress fracture and determining its severity. Treatment involves rest, immobilization, pain management, and, in some cases, physical therapy. Following the healthcare professional’s recommendations and allowing adequate time for the bone to heal is crucial for a successful recovery.
Preventing stress fractures involves adopting proper training techniques, wearing appropriate footwear, and maintaining overall bone health. Gradually increasing activity levels, incorporating rest days, and ensuring adequate nutrition are essential for preventing overuse injuries. Seeking medical attention at the first sign of symptoms is crucial for early intervention and preventing further complications.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for stress fracture bruises, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their foot health and prevent future injuries. Maintaining a balance between physical activity and rest, wearing supportive footwear, and prioritizing overall bone health are key strategies for ensuring the longevity and well-being of your feet.